
Geo-Eye
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geo-Eye
Year: 2021, Volume: 10, Issue: 1, Pages: 27-32
Original Article
Basavaraj R Bagade1*, Anupama Dubey2
1Assistant Professor, Department of studies in Geography, Rani Channamma University, Belagavi, Karnataka, India
2Assistant Professor, Center for Sustainable Development, Institute of Public Enterprises, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:07 February 2021, Accepted Date:22 April 2021
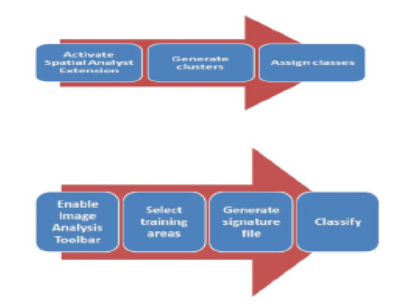
This paper examines the use of GIS and Remote Sensing in mapping Land Use Land Cover in Bagalkot district. The land use/land cover (LULC) pattern of a region in time and space is an outcome of natural and socio-economic factors and their utilization by man after construction Upper Krishna Project in Bagalkot city change in the land use land cover in Bagalkot city Karnataka, land use system is not a homogeneous process. Hence, land use manipulation by human beings is widespread and has become a serious threat to watershed services including stream flow regulation, soil erosion control, and low-flow augmentation at both micro-and macro-level catchments. The Understanding of Land Use through supervised and unsupervised classification of Land use by using RS and GIS technology helps in understanding the driving mechanism that causes land-use change. Therefore, an attempt will make to prepare LULC map of Bagalkot city, Karnataka by using Supervised and unsupervised classification. The classification will be developing through an unsupervised classification approach that will find prominent features of the area. However, analysis of supervised classification from multitemporal satellite imageries estimated 10 land use/ land cover. With respect to the rate of changes in the Bagalkot city. Bagalkot city is in the northern part of Karnataka state, situated in the interior of the Deccan Plateau or Bailusime region. The introduction of planning to Indian cities has been the most recent phenomena. The creation of linguistic states necessitated the construction of planned cities, some of them completely fresh. This included Chandigarh, the most notable example, Bhubaneshwar, Gandhinagar, Dispur and Bokaro, for administrative purposes and Navi Mumbai, New Bangalore, Noida for catering further expansion of the city. Navanagar Resettlement plan consists of acquisition of lands for locating the new Bagalkot town and making all arrangements to provide basic infrastructure in the new town. The plan of new township provides adequate and reasonable resettlement for the project displaced families and also allows sufficient scope for further development of the town for additional population. Hence, The Understanding of Land Use through supervised and unsupervised classification of Land use by using RS and GIS technology help in understanding the driving mechanism that causes land use change. Therefore, an attempt is made to prepare since this study is time-bound, the researcher has selected an area that is geographically small and easily manageable from thepoint of investigation and analysis.
Keywords: GIS technology; supervised; unsupervised classification; LnadUse Landcover
© 2021 Bagade & Dubey. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.