
Geo-Eye
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geo-Eye
Year: 2022, Volume: 11, Issue: 1, Pages: 6-11
Original Article
Suzan Karmoka1, Ashok D Hanjagi1,*
1 Department of Geography, Bangalore University, Jnana Bharathi, Bengaluru, 560056, Karnataka, India
*Corresponding author email: [email protected]
Received Date:16 January 2022, Accepted Date:18 May 2022
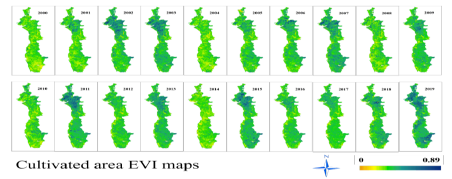
The study aims to determine the vegetation covers (natural and cultivated) affected by precipitation amounts in the Syrian coastal area from 2000 to 2019, and for this, precipitation data for 23 climatic stations were used, in addition to the spectral vegetation indices EVI and LAI from the MODIS satellite. The results showed that vegetation covers are affected by the amount of precipitation, but there is a difference in vulnerability degree in the cultivated and natural cover (forests). The cultivated vegetation covers were more affected by the decrease or increase in the precipitation amount, as the area is coastal and depends heavily on rainwater. The cultivated cover has declined significantly in the years with low precipitation, especially the years 2008, 2010, 2014 2016, while it responded well to the high precipitation values in 2003, 2012, 2015 and 2019. While the forests showed a slight impact on the decrease in the amount of precipitation due to their nature of adaptation to the conditions of the region, where most of the years maintained stable and high values for both EVI and LAI indices, except for 2014 and 2016 which were the years with the sharp decline in the amount of precipitation. When the forests were affected by the decline in precipitation in addition to the fires resulting from the crisis conditions in Syria, which increased the severity of damage in forest cover. This indicates that the forests were affected in the first place as a result of fires and in the second place as a result of precipitation, while the cultivated cover was mainly affected by the lack of precipitation.
Keywords
Coastal area, EVI, Forests, LAI, Precipitation, Vegetation cover
© 2022 Karmoka & Hanjagi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.