
Geo-Eye
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geo-Eye
Year: 2022, Volume: 11, Issue: 2, Pages: 9-14
Original Article
Salma Sultana1, M Inayathulla 2,*
1 Research Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, Bangalore University, Bangalore
2 Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Bangalore University, Bangalore
*Corresponding author email: [email protected]
Received Date:18 August 2022, Accepted Date:22 November 2022
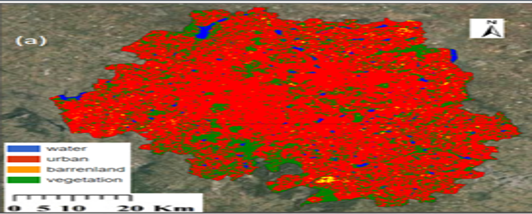
Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) classification plays a pivotal role in understanding and managing environmental resources. This study presents a novel methodology utilizing sentinel satellite data in conjunction with two robust machine learning algorithms: Random Forest (RF) and Support Vector machine (SVM) on Google Earth Engine platform. Sentinel data, renowned for its high- resolution multispectral imagery, provides rich information for classification. Google Earth Engine provides access to vast geospatial datasets and computational resource, enabling effective analysis. RF and SVM, distinguished for their ability to handle complex dataset, are employed to optimize classification accuracy. A systematic work flow for preprocessing of Sentinel imagery is outlined, followed by implementation of RF and SVM algorithm with a focus on accurately classifying vegetation, built-up areas, barren land and water bodies. Evaluation metrics including overall accuracy and kappa coefficient demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed methodology. A compelling study demonstrates the utility of RF and SVM within GEE for precise LULC mapping, highlighting their pivotal role in supporting informed decision-making for environmental planning and conservation initiatives.
Keywords
GEE, SVM, RF, Sentinel Data, LULC
Bangalore
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.