
Geo-Eye
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geo-Eye
Year: 2022, Volume: 11, Issue: 2, Pages: 31-36
Original Article
A Arathy1, V Nischitha1
1 Department of Geography, Bangalore University, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Received Date:15 September 2022, Accepted Date:27 November 2022
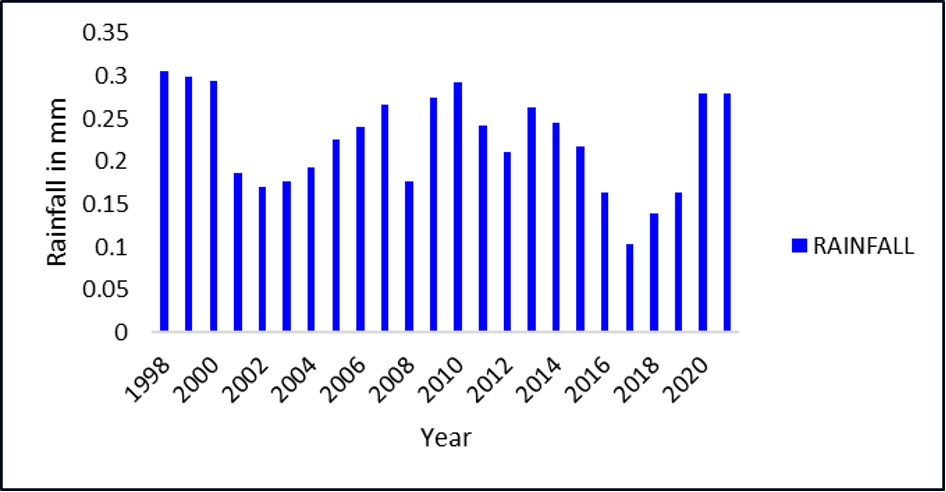
Climate change has caused significant variations in precipitation across the different geographical regions of the world. A better understanding of rainfall trends, distribution, and features is essential for effective water resource management, particularly in areas with high spatiotemporal variability. This study examines the spatiotemporal changes in rainfall patterns of the Tunga River Basin which is located in the Western Ghats region of Karnataka, India. Also, the potential reasons for the rainfall variability in the region were investigated. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) 3B43 monthly precipitation data for 24 years from 1998 to 2021 were used. The study revealed that the high-elevated areas are getting more rainfall compared to the lowlands, which shows the influence of topography on precipitation.
Keywords
IDW, Rainfall, Spatial variability, Temporal variability, TRMM
© 2022. Arathy & Nischitha. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.