
Geo-Eye
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geo-Eye
Year: 2024, Volume: 13, Issue: 1, Pages: 15-22
Original Article
T K Prasad∗, K P Shimod, V Vineeth Kumar, M Manjuladevi
∗Corresponding author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:05 March 2024, Accepted Date:08 March 2024
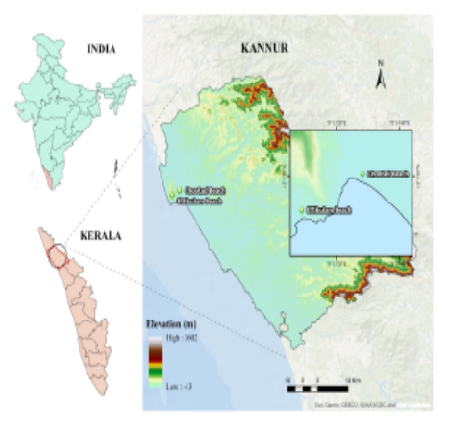
Radioactivity is an essential part of earth and it influences the environment. There are different geographical processes are included the concentration and distribution of natural radionuclides such as weathering, erosion, deposition, leaching, volcanism, mass wasting, weathering of rocks and soils. High background radiation is cause for the long lifetime risk such as the cancer, cardiovascular disease etc. Monitoring of radioactive elements is the uttermost importance for the humankind and environmental protection. Similarly it also provides helpful information to evaluate the dose to the humankind to identify the health risk and to have baseline data for future changes. And it give the radiological parameters such as the absorbed dose rate, indoor annual effective dose rate, outdoor annual effective dose rate, excess lifetime cancer risk for analyses the lifetime risk in that region. This study is to assess the cancer health risk of Chootad beach and Ettikulam beach in Kannur district of Kerala, India. The radiological parameters are estimated using Micro – R survey meter (Scintillometer) and the mean values of excess lifetime cancer risk are compared with the world and national average.
Keywords: Radioactivity, Regional Geomorphology, Excess Life Time Cancer Risk (ELCR), Radiological Parameters
Academic Journals. (n.d.). Retrieved July 31, 2021, from AG, U., S Ben, B., JP, A., & PJ, J. (2016). External dose measurements in the Eloor industrial area in the Ernakulam district of Kerala, India.
Akram, M., Qureshi, R. M., Ahmad, N., & Solaija, T. J. (2006). Gamma-emitting radionuclides in the shallow marine sediments off the Sindh coast, Arabian Sea. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 118(4), 440–447.
Assessment of lifetime cancer risk from natural radioactivity levels in Kadikoy and Uskudar District of Istanbul . SpringerLink.
Balakrishnan, D., Umadevi, A. G., Byju, S. B., Sunil, A., Abraham, J. P., Jojo, P. J., Radhakrishnan, S., & Harikumar, M. (2016). External dose measurements in the Eloor industrial area in the Ernakulam district of Kerala, India. International Journal of Radiation Research, 14(4), 323.
Divya, P. V., Kaliprasad, C. S., Narayana, Y., & Prakash, V. (2019). Distribution of natural radionuclides and assessment of excess lifetime cancer risk along coastal areas of Varkala in Kerala. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 322(1), 121–127.
Durusoy, A., & Yildirim, M. (2017). Determination of radioactivity concentrations in soil samples and dose assessment for Rize Province, Turkey. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 10(4), 348–352.
Ezekiel, A. O. (2017). Assessment of excess lifetime cancer risk from gamma radiation levels in Effurun and Warri city of Delta state, Nigeria. Journal of Taibah University for Science, 11(3), 367–380
Ihsan, K., Qin, Z., Tianci, X., Bin, Z., Li, H., Sun, W., & Lewis, E. (2020). Evaluation of health hazards from radionuclides in soil and rocks of North Waziristan, Pakistan. Iranian Journal of Radiation Research, 18, 243–253.
Narayana, Y., & Rajashekara, K. M. (2010). The importance of physico-chemical parameters on the speciation of natural radionuclides in riverine ecosystems. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 101(11), 958–964.
Narayana, Y., Rajashekara, K. m., & Siddappa, K. (2007a). Activity of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K in riverine environs and evaluation of radiological hazards. International Journal of Low Radiation, 4(3), 200–208.
Narayana, Y., Rajashekara, K. M., & Siddappa, K. (2007b). Natural radioactivity in some major rivers of coastal Karnataka on the southwest coast of India. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 95(2), 98–106.
Narayana, Y., Shetty, P. K., & Siddappa, K. (2005). Enrichment of natural radionuclides in monazite areas of coastal Kerala. International Congress Series,
Prakash, M. M., Kaliprasad, C. S., & Narayana, Y. (2017a). Distribution of 210Po in soils of Virajpet taluk, Coorg District, Karnataka. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 10(1), 57–62
Prakash, M. M., Kaliprasad, C. S., & Narayana, Y. (2017b). Studies on natural radioactivity in rocks of Coorg district, Karnataka state, India. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 10(2), 128–134.
Prakash, V., Rajashekara, K. M., & Narayana, Y. (2014). A study on enrichment pattern and depth profile of natural radionuclides in monazite areas of coastal Karnataka, India. Proceedings of the Thirty First IARP National Conference on Advances in Radiation Measurement Systems and Techniques: Abstract Book.
Prakash, V., Rajashekara, K. M., & Narayana, Y. (2018). Study on effects of physicochemical parameters on natural radionuclides concentration and assessment of radiological parameters in the soil samples of Mangalore, Dakshina Kannada. Radiation Protection and Environment, 41(4), 192.
SureshGandhi, M., Ravisankar, R., Rajalakshmi, A., Sivakumar, S., Chandrasekaran, A., & Pream Anand, D. (2014). Measurements of natural gamma radiation in beach sediments of north east coast of Tamilnadu, India by gamma ray spectrometry with multivariate statistical approach. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 7(1), 7–17.
© 2024 Prasad et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.